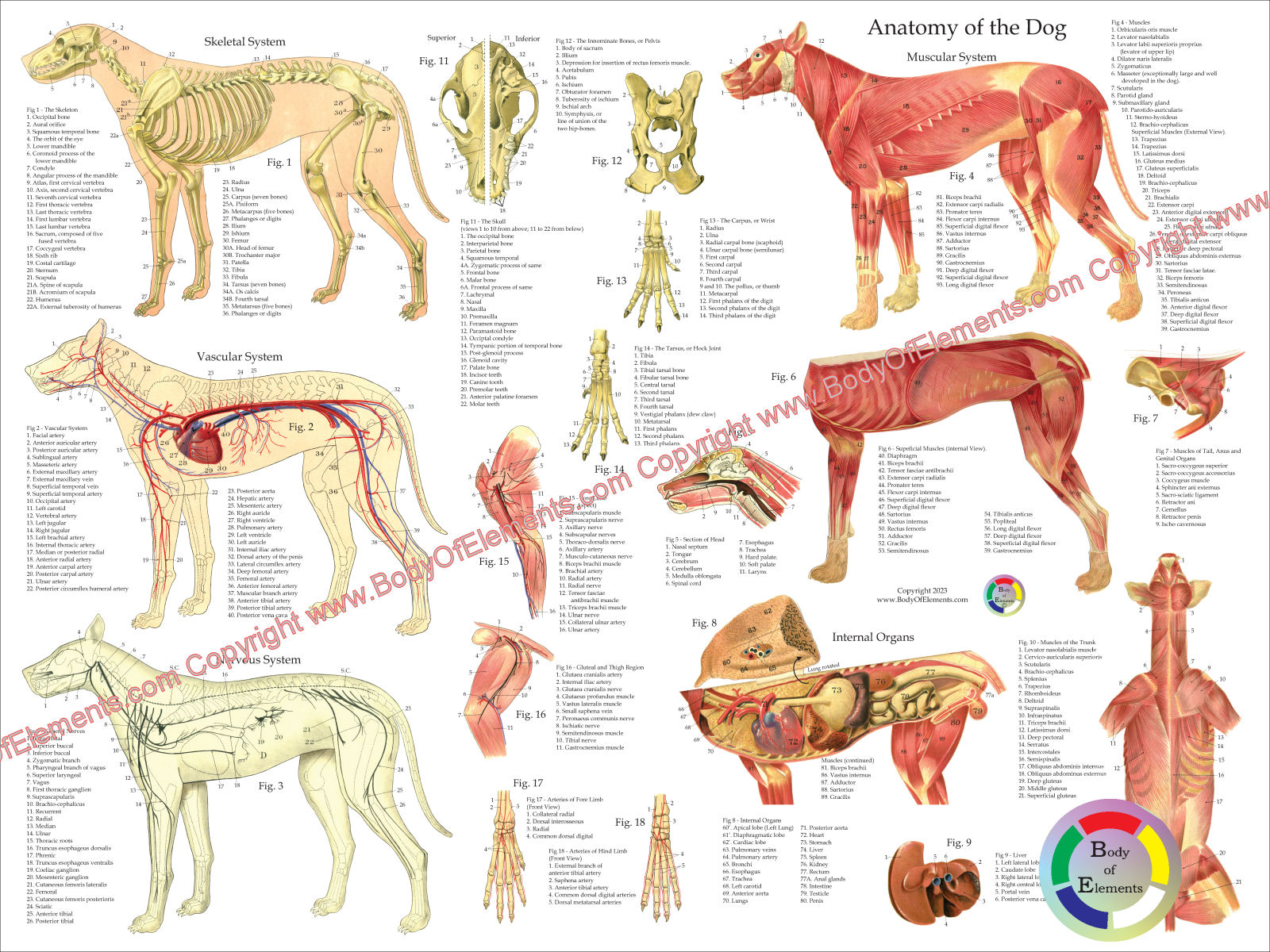
Anatomy Of Dog Tail - Lateral flexion of the tail.
Anatomy Of Dog Tail - A dog’s tail is part of the spinal column. It contains multiple vertebral segments (bones) that progress from larger to smaller from the base of the tail toward the tip. Here’s a quick dog tail anatomy lesson: A dog's tail contains vertebrae, muscles, nerves, blood vessels and cartilage or bone. The tail also includes muscles that enclose the bones, as well as tendons and nerves.
Highlights suggested a tail is a string of bones [vertebrae] like a string of beads, and that there are muscles attached to the bones. A dog tail is essentially an extension of the dog’s backbone. You will get the detailed anatomy of the dog tail bone, muscle, and artery with a diagram. The belly or abdomen is the underside of the dog from the end of its rib cage to its tail. The tail is an important part of the canine anatomy and is actually an extension of the spine. The tail muscle and nerves facilitate tail movement. A key part of a dog's anatomy is the tail.
Dog Anatomy List of Useful Parts of a Dog From Head to Tail Dog
Branches of the plexus caudalis ventralis. The tail muscle and nerves facilitate tail movement and play a role in bowel control. Dog tails are made of vertebrae, muscles, cartilage, and nerves. The main purpose of a dog's tail is for communication and balance. When a dog barks, it contracts the diaphragm forcefully to expel air.
Dog Anatomy Tail
When a dog barks, it contracts the diaphragm forcefully to expel air out of its lungs and through its vocal cords. A dog’s bones are denser than a human’s bones. Tails are made up of vertebrae just like the backbone. The tail muscle and nerves facilitate tail movement. It’s made up of several smaller bones.
Do Dogs' Tails Have Bones? Exploring the Anatomy of Man's Best Friend
You will get the detailed anatomy of the dog tail bone, muscle, and artery with a diagram. A dog’s spine does not have the natural curve that the human spine does. Lateral flexion of the tail. A dog tail is essentially an extension of the dog’s backbone. Serving healthcare professionals through interactive anatomy atlases, medical.
Dog skeleton 101 Dog Anatomy Bones Animal Hackers
Highlights suggested a tail is a string of bones [vertebrae] like a string of beads, and that there are muscles attached to the bones. Compared to a dog’s skull, the human skull is larger to hold a larger brain and sits vertically rather than horizontally. Learn dog tail anatomy with a labeled diagram. Tails are.
Dog Tail Anatomy Anatomy Reading Source
Understanding the reasons behind their tails can provide insight into the behavior and communication of these animals. The tail is an important part of the canine anatomy and is actually an extension of the spine. The tail muscle and nerves facilitate tail movement and play a role in bowel control. The loin is the back.
+28 Anatomy Of Dog Tail Ideas
Here’s a quick dog tail anatomy lesson: Lateral flexion of the tail. The number of caudal vertebrae in a dog’s tail is highly variable. Acting together they facilitate a. Branches of the plexus caudalis ventralis. A dog’s bones are denser than a human’s bones. Understanding the reasons behind their tails can provide insight into the.
11 Dog Tail Shapes & 10 Impressive facts about Dog Tail √ The Secrets
The diaphragm is the primary muscle involved in breathing. Ventral surface of each caudal vertebra. Serving healthcare professionals through interactive anatomy atlases, medical imaging, collaborative database of clinical cases, online courses. A dog’s tail is composed of a sequence of small, bony segments, known as vertebrae, that extend from the base of the spine. Dog.
Do Dogs Have Bones in Their Tails?
Acting together they facilitate a. The tail is an important part of a dog`s anatomy and is actually an extension of the spine. Canine tails are the last segment of the spine and are made up of as many as 23 vertebrae that get progressively smaller from base to tip. Dog tail anatomy the tail.
Dog Tail Anatomy Anatomy Reading Source
Here’s a quick dog tail anatomy lesson: Highlights suggested a tail is a string of bones [vertebrae] like a string of beads, and that there are muscles attached to the bones. The shape of a dog’s tail can help you figure out if your dog may be at risk for particular health concerns. The anatomy.
Dog Anatomy Poster
We will tell you about the general structure of the tail, how the tail works in dogs, common diseases that affect the tail and common diagnostic tests performed in dogs to evaluate the tail. In this ultimate guide to dog tail types, we will delve into the anatomy of a dog’s tail and why it.
Anatomy Of Dog Tail A dog’s tail is part of the spinal column. The tail also includes muscles that enclose the bones, as well as tendons and nerves. Here’s a quick dog tail anatomy lesson: Imaios is a company which aims to assist and train human and animal practitioners. It’s made up of several smaller bones known as vertebrae, covered in skin, muscle, and fur.
That’s A Nice Generalization Suitable For Kids, But Let’s Try To Go Just A Little Past That.
The tail muscle and nerves facilitate tail movement and play a role in bowel control. Dog tails are made of vertebrae, muscles, cartilage, and nerves. A dog’s bones are denser than a human’s bones. When a dog barks, it contracts the diaphragm forcefully to expel air out of its lungs and through its vocal cords.
In This Ultimate Guide To Dog Tail Types, We Will Delve Into The Anatomy Of A Dog’s Tail And Why It Is Essential To Understand Different Types.
Soft discs cushion the spaces between the vertebrae and allow flexibility. A dog’s tail is part of the spinal column. This is usually for aesthetics, although some working dogs may have them docked to protect them from being caught. Highlights suggested a tail is a string of bones [vertebrae] like a string of beads, and that there are muscles attached to the bones.
Understanding The Reasons Behind Their Tails Can Provide Insight Into The Behavior And Communication Of These Animals.
Ecvdi, utrecht, netherland) were categorized topographically into seven chapters (head, vertebral column, thoracic limb, pelvic limb, larynx/pharynx, thorax and. The anatomy of a dog tail. A dog’s tail also consists of muscles that attach to the vertebrae that help to control the conscious movement of the tail. The tail is an important part of a dog`s anatomy and is actually an extension of the spine.
The Flank Refers To The Side Of The Dog Between The End Of The Chest And The Rear Leg.
This limb is often cut by certain breeders in a process known as ‘docking’. Branches of the plexus caudalis ventralis. The loin is the back between the end of the rib cage and the beginning of the pelvic bone. Dog tail anatomy the tail of a dog serves many functions such as non verbal communication and as a rudder in water.