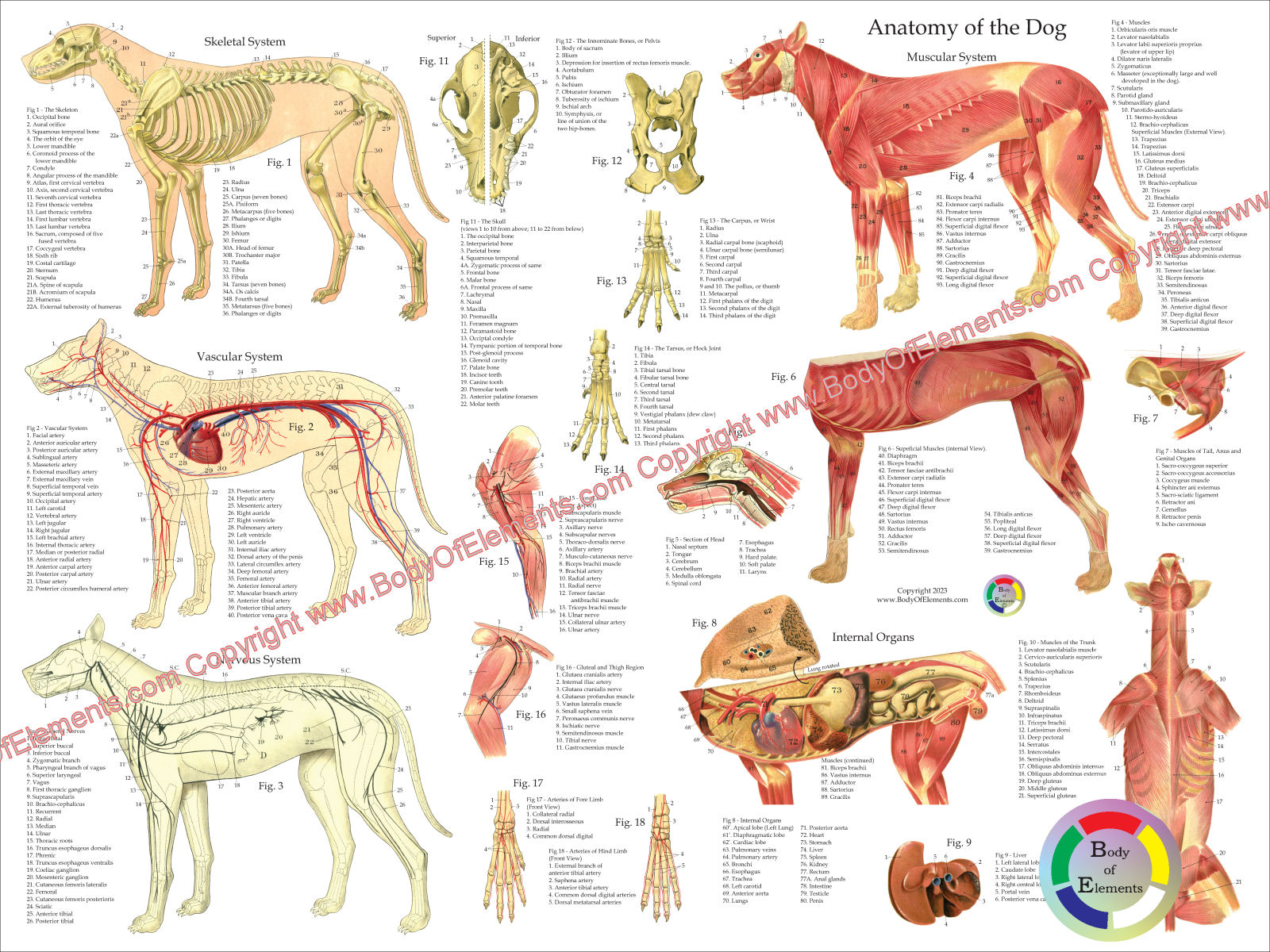
Dogs Internal Anatomy - Gain a comprehensive understanding of your dog's health with our veterinary guide to cat anatomy complete with diagrams, images and simple explanations.
Dogs Internal Anatomy - The cerebrum is the part of the dog's brain which performs functions such as learning. A dog’s spine does not have the natural curve that the human spine does. Ecvdi, utrecht, netherland) were categorized topographically into seven chapters (head, vertebral column, thoracic limb, pelvic limb, larynx/pharynx, thorax and. The internal anatomy of dogs, is very similar to the anatomy of other carnivorous mammals such as the cat. The throat is beneath the jaws.
Facilitates the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide, allowing for proper breathing and gas exchange. Their bodies are made up of many different parts, including their skeleton, muscles and internal organs. Dog anatomy ©sheri amsel www.exploringnature.org stomach lungs kidney colon esophagus heart small intestine trachea spleen bladder liver ©sheri amsel www.exploringnature.org label the dog organs. Labeled images in the transverse plane of a healthy dog’s whole body, using tomodensitometry. Some of the different canine joints are labeled. Seat of the intelluctual capacities of a gog. Muscle, organ and skeletal anatomy).
Dog Digestive Process and what the stages are and how it works
You can also view the spinal column and the brain. You will find four lobes in the right lung and two in the left lung of a dog. The internal anatomy of dogs, is very similar to the anatomy of other carnivorous mammals such as the cat. Carnivorous domestic mammal raised to perform various tasks.
Dogs Internal Organs Diagram
Facilitates the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide, allowing for proper breathing and gas exchange. Anatomy atlas of the canine general anatomy: Muscle, organ and skeletal anatomy). Details of structures vary tremendously from breed to breed, more than in any other animal species, wild or domesticated, [1] as dogs are highly variable in height and.
Dog Internal Anatomy Anatomical Charts & Posters
The gastrointestinal tract in dogs includes the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Dog anatomy comprises the anatomical study of the visible parts of the body of a domestic dog. Internal anatomy of a dog: Here are presented scientific illustrations of the canine muscles and skeleton from different anatomical standard views (lateral, medial, cranial, caudal, dorsal, ventral.
Canine Internal Anatomy Chart. Anatomy of Dog with Inside Organ
Their bodies are made up of many different parts, including their skeleton, muscles and internal organs. The internal organs of a dog include the heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, stomach, intestines, and reproductive organs. What are the internal organs of a dog? Facilitates the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide, allowing for proper breathing and gas.
Poster organe interne caine Tuvet
The dog heart is placed obliquely at the level between the third rib and to sixth intercostal space. The major internal organ systems in canine anatomy include: From their skeletal system to their muscular and internal organ systems, understanding canine anatomy is essential for veterinarians, dog owners, and anyone working with or studying dogs. On.
Dog Internal Anatomy Diagram
Here, i will discuss the external parts of a dog and their functions with a diagram. Dog anatomy comprises the anatomical study of the visible parts of the body of a domestic dog. On the left side view of a dog's internal organs, you can see the lungs, heart, liver, stomach, spleen, kidney, intestines, bladder,.
Dog anatomy Royalty Free Vector Image VectorStock
One of the most important parts of. The internal organs of a dog include the heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, stomach, intestines, and reproductive organs. From their skeletal system to their muscular and internal organ systems, understanding canine anatomy is essential for veterinarians, dog owners, and anyone working with or studying dogs. Important part of the.
Dog Anatomy The Y Guide
Part of the digestive tract between the esophagus and the intestine. Here, i will discuss the external parts of a dog and their functions with a diagram. Some fascias, tendons, ligaments, joints were labeled. A dog’s spine does not have the natural curve that the human spine does. Labeled images in the transverse plane of.
Dog Internal Anatomy Poster 24 x 36
The crest starts at the nape and ends at the withers (see the last item in this list). Responsible for circulating blood and delivering oxygen and nutrients to the body’s tissues. The dog heart is placed obliquely at the level between the third rib and to sixth intercostal space. One of the most important parts.
Internal Organs Of A Male Dog. From Photograph by Ken Welsh
A dog's physical anatomy is designed to help them navigate their environment and perform various tasks. Humans have 206 bones compared to approximately 319 in dogs. Though it is a very basic topic, it is great for a veterinarian to describe a dog’s conformation. Anatomy atlas of the canine general anatomy: The cerebrum is the.
Dogs Internal Anatomy Details of structures vary tremendously from breed to breed, more than in any other animal species, wild or domesticated, [1] as dogs are highly variable in height and weight. The major internal organ systems in canine anatomy include: Humans have 206 bones compared to approximately 319 in dogs. Canine anatomy is a complex and fascinating subject that encompasses the structure and function of a dog’s body. A dog’s spine does not have the natural curve that the human spine does.
What Are The Internal Organs Of A Dog?
Internal anatomy of a dog: You will find four lobes in the right lung and two in the left lung of a dog. The detailing of these structures changes based on dog breed due to the huge variation of size in dog breeds. From their skeletal system to their muscular and internal organ systems, understanding canine anatomy is essential for veterinarians, dog owners, and anyone working with or studying dogs.
Facilitates The Exchange Of Oxygen And Carbon Dioxide, Allowing For Proper Breathing And Gas Exchange.
Here are presented scientific illustrations of the canine skeleton, with the main dog's bones and its structures displayed from different anatomical standard views (cranial, caudal, lateral, medial, dorsal, palmar.). Here are presented scientific illustrations of the canine muscles and skeleton from different anatomical standard views (lateral, medial, cranial, caudal, dorsal, ventral / palmar.). Dog anatomy comprises the anatomical study of the visible parts of the body of a domestic dog. Keep reading to learn about the different body parts in dogs, and how each works in your dog's everyday life.
A Dog’s Spine Does Not Have The Natural Curve That The Human Spine Does.
Dog anatomy details the various structures of canines (e.g. The following paragraphs explain all these aspects in brief, along with diagrams, which will help you understand them better. Seat of the intelluctual capacities of a gog. The major internal organ systems in canine anatomy include:
Some Of The Different Canine Joints Are Labeled.
Positional and directional terms, general terminology and anatomical orientation are. On the left side view of a dog's internal organs, you can see the lungs, heart, liver, stomach, spleen, kidney, intestines, bladder, and the rectum in that order from front to back. 25/04/2023 10/02/2022 by sonnet poddar. The dog heart is placed obliquely at the level between the third rib and to sixth intercostal space.