Pancreas Ultrasound Anatomy - 2) mistakes related to anatomical structures localized in the vicinity of the pancreas (caudate lobe of the liver, other organ.
Pancreas Ultrasound Anatomy - Often, even with a valiant. Marc engelbrecht, jennifer bradshaw and robin smithuis. Anatomy, physiology & ultrasound appearance :: Thus the spleen can be used as a window and a left intercostal coronal approach can. The pancreas is an extended, accessory digestive gland that is found retroperitoneally, crossing the bodies of the l1 and l2 vertebrae on the posterior abdominal wall.
12k views 2 years ago normal abdomen. The pancreas is an extended, accessory digestive gland that is found retroperitoneally, crossing the bodies of the l1 and l2 vertebrae on the posterior abdominal wall. The pancreas is a large gland in the back of your abdomen (belly). 1) mistakes related to the anatomical structure of the pancreas (anatomical variants, echostructure and echogenicity, course of the splenic artery); At least three gray scale images of the right. Often, even with a valiant. Optimal transducer selection, patient positioning, imaging approaches, and techniques for sonographically evaluating the pancreas are discussed.
Ultrasound of the Pancreas Radiology Key
Strategies to see the pancreas include using the left hepatic lobe as an acoustic window, imaging an npo patient (not usually possible), or pressing on the abdomen firmly to push away overlying air (not always comfortable). Pancreatic ultrasound can be used to assess for pancreatic malignancy, pancreatitis and its complications, as well as for other.
Normal Pancreas Ultrasound
It is important to start the ultrasound examination with an evaluation of the pancreas before the child swallows air by talking or crying, and before air normally migrates toward the gastric antrum and transverse colon. Often, even with a valiant. 1) mistakes related to the anatomical structure of the pancreas (anatomical variants, echostructure and echogenicity,.
Pancreas Ultrasound Anatomy
As ultrasound (us) is simple and less invasive than other imaging modalities, this technique is widely used for mass screening. Radiology department of the academical medical centre, amsterdam and the alrijne hospital in leiderdorp, the netherlands. The anatomy of the pancreas and surrounding structures is critical for understanding the surgical indications and contraindications for pancreatic.
Pancreas Ultrasound Labeled
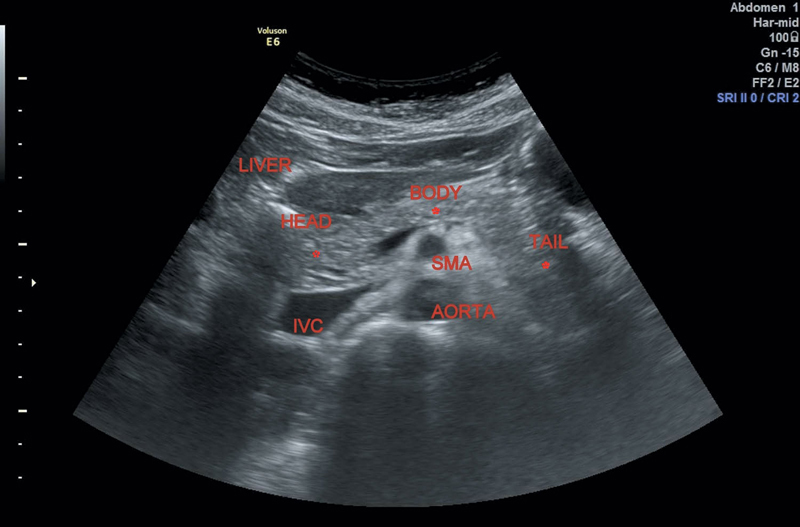
Radiology department of the academical medical centre, amsterdam and the alrijne hospital in leiderdorp, the netherlands. The use of high frequency, even linear transducers, usually results in detailed images of all pancreatic areas. Similar content being viewed by others. The longest part of the pancreas is located to the left of the midline, with the.
Pancreas Ultrasound Labeled
Ultrasound is the first modality used in the evaluation of pancreatic disease. Strategies to see the pancreas include using the left hepatic lobe as an acoustic window, imaging an npo patient (not usually possible), or pressing on the abdomen firmly to push away overlying air (not always comfortable). Similar content being viewed by others. Pancreatic.
Pancreas Radiology Key
Download reference work entry pdf. The pancreas is easily investigated in children thanks to the relative lack of fat tissue and the large left hepatic lobe with an optimal acoustic window. The pancreas is distinguished on ultrasound by its uniquely glandular parenchyma; However, since its echogenicity varies with age and disease process, it is most.
Pancreas Ultrasound Labeled
1) mistakes related to the anatomical structure of the pancreas (anatomical variants, echostructure and echogenicity, course of the splenic artery); Radiology department of the academical medical centre, amsterdam and the alrijne hospital in leiderdorp, the netherlands. The errors and mistakes in question were divided into three categories: The anatomy of the pancreas and surrounding structures.
Abdominal ultrasound
2) mistakes related to anatomical structures localized in the vicinity of the pancreas (caudate lobe of the liver, other organ. As ultrasound (us) is simple and less invasive than other imaging modalities, this technique is widely used for mass screening. Optimal transducer selection, patient positioning, imaging approaches, and techniques for sonographically evaluating the pancreas are.
Ultrasound of the Pancreas Radiology Key
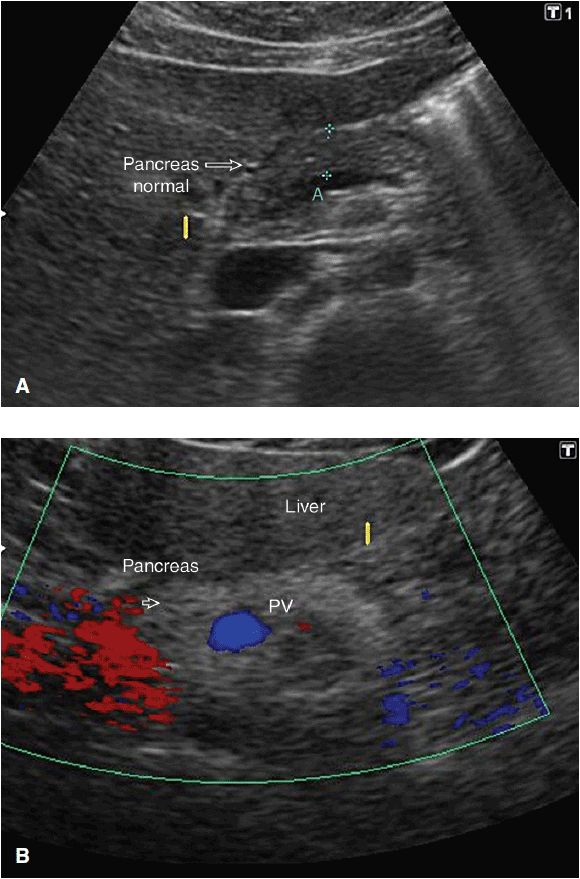
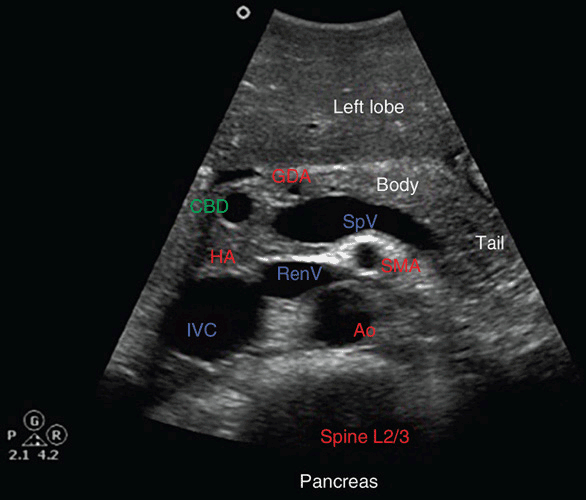
However, visualizing the entire pancreas due to complicated anatomy, obesity and overlying gas can be difficult. Use the splenic vein to help identify the pancreas superficial to this. Marc engelbrecht, jennifer bradshaw and robin smithuis. The pancreas is an extended, accessory digestive gland that is found retroperitoneally, crossing the bodies of the l1 and l2.
Ultrasound of pancrease in Radiology
The errors and mistakes in question were divided into three categories: Strategies to see the pancreas include using the left hepatic lobe as an acoustic window, imaging an npo patient (not usually possible), or pressing on the abdomen firmly to push away overlying air (not always comfortable). Anatomy, physiology & ultrasound appearance :: Optimal transducer.
Pancreas Ultrasound Anatomy Often, even with a valiant. Learn how to use ultrasound to evaluate the pancreas, including pancreas anatomy and physiology and sonographic anatomy of the pancreas. Your pancreas is a dual organ — like a factory with two production lines. The errors and mistakes in question were divided into three categories: Marc engelbrecht, jennifer bradshaw and robin smithuis.
The Pancreas Can Be Visualized At Us In Most Patients, Independent Of Gastrointestinal Gas Interference And Fat.
Download reference work entry pdf. To put it in a clinical context, its oblique position makes it impossible to see the entire pancreas in a single transverse section. The pancreas lies transversely in the upper abdomen between the duodenum on the right and the spleen on the left. Thus the spleen can be used as a window and a left intercostal coronal approach can.
The Pancreas Is Easily Investigated In Children Thanks To The Relative Lack Of Fat Tissue And The Large Left Hepatic Lobe With An Optimal Acoustic Window.
As ultrasound (us) is simple and less invasive than other imaging modalities, this technique is widely used for mass screening. Anatomy should be intentionally imaged in an organized fashion and correctly labeled for clarity. Learn how to use ultrasound to evaluate the pancreas, including pancreas anatomy and physiology and sonographic anatomy of the pancreas. The longest part of the pancreas is located to the left of the midline, with the tail near the splenic hilum usually slightly above the head.
Often, Even With A Valiant.
It’s part of your digestive system and your endocrine system. In this way, the presence of bowel gas is limited, the stomach is empty of food, and the entire organ can be visualized. Citation, doi, disclosures and article data. The errors and mistakes in question were divided into three categories:
Radiology Department Of The Academical Medical Centre, Amsterdam And The Alrijne Hospital In Leiderdorp, The Netherlands.
Pancreas anatomy & physiology ultrasound training. Your pancreas is a dual organ — like a factory with two production lines. Use the splenic vein to help identify the pancreas superficial to this. Ultrasound is the first modality used in the evaluation of pancreatic disease.