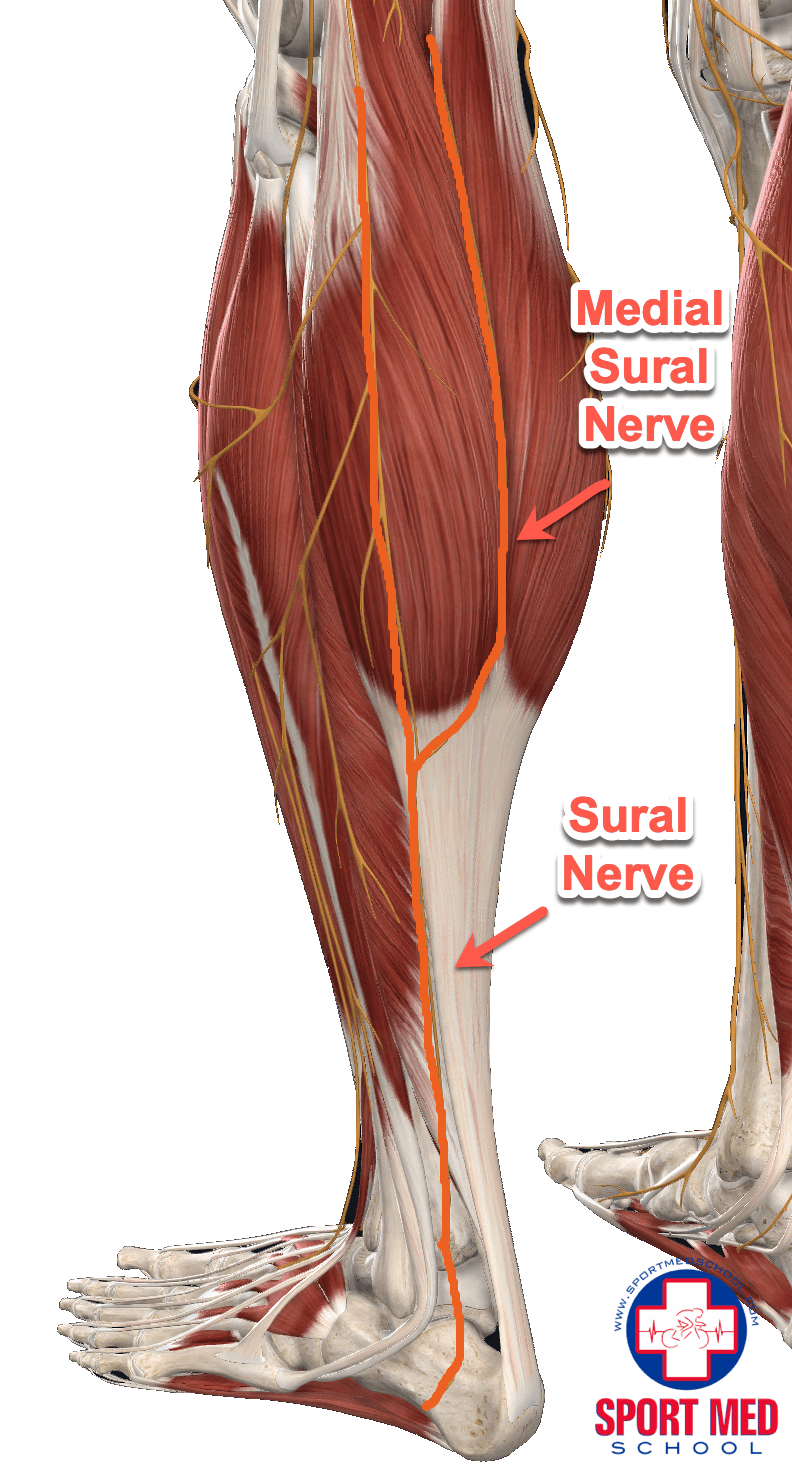
Sural Region Anatomy - For more information, please refer to the description of the posterior leg region.
Sural Region Anatomy - Many health conditions can affect your nerve, including diabetes and sports injuries. The sural region pertains to the posterior leg region. For more information, please refer to the description of the posterior leg region. The sural nerve passes through the calf (sural region) superficial to the gastrocnemius muscle and lateral to the calcaneal (achilles) tendon. At the distal third of the gastrocnemius, both sural cutaneous branches join to become the sural nerve.
It is formed by terminal branches of the tibial and common peroneal nerves that join together in the superficial aspect of the distal third of the leg. For more information, please refer to the description of the posterior leg region. The sural nerve passes through the calf (sural region) superficial to the gastrocnemius muscle and lateral to the calcaneal (achilles) tendon. Your sural nerve’s length and ability to regenerate make it ideal for a sural nerve biopsy or graft. As it crosses the ankle joint, it passes posterior to the lateral malleolus and turns to run along the lateral side of the foot. It is formed by the union of two smaller sensory nerves: The sural nerve (sn) is an important pure sensory cutaneous nerve which innervates the lateral ankle and foot to the base of the fifth metatarsal.
Sural Nerve Clinical Gate
It provides sensation to your lower leg and parts of your foot. It supplies the skin over the posterolateral leg and foot. The medial sural cutaneous nerve (a branch of the tibial nerve ), and lateral sural cutaneous nerve (branch of the common fibular nerve ). The sural nerve passes through the calf (sural region).
Sural Nerve Anatomy Orthobullets vrogue.co
At the distal third of the gastrocnemius, both sural cutaneous branches join to become the sural nerve. It is formed by terminal branches of the tibial and common peroneal nerves that join together in the superficial aspect of the distal third of the leg. The sural nerve is a cutaneous nerve, providing only sensation to.
Sural Region
Your sural nerve’s length and ability to regenerate make it ideal for a sural nerve biopsy or graft. It is formed by the union of two smaller sensory nerves: It supplies the skin over the posterolateral leg and foot. It provides sensation to your lower leg and parts of your foot. The medial sural cutaneous.
Sural Nerve Anatomy
Descends on the posterolateral aspect of leg. It supplies the skin over the posterolateral leg and foot. Travels posterior to lateral malleolus and deep to fibularis tendon sheath. It is formed by the union of two smaller sensory nerves: For more information, please refer to the description of the posterior leg region. The sural nerve.
Sural Nerve Entrapment Sport Med School
Many health conditions can affect your nerve, including diabetes and sports injuries. It is formed by terminal branches of the tibial and common peroneal nerves that join together in the superficial aspect of the distal third of the leg. Travels posterior to lateral malleolus and deep to fibularis tendon sheath. The sural region pertains to.
Sural Region
The sural nerve is a cutaneous nerve of the lower limb, formed by contributions from the tibial and common fibular nerves. The sural nerve is a cutaneous nerve, providing only sensation to the posterolateral aspect of the distal third of the leg and the lateral aspect of the foot, heel, and ankle. This union may.
Sural Anatomy
At the distal third of the gastrocnemius, both sural cutaneous branches join to become the sural nerve. This union may happen at variable levels in the posterior compartment of the leg. Descends on the posterolateral aspect of leg. As it crosses the ankle joint, it passes posterior to the lateral malleolus and turns to run.
Sural Nerve Anatomy Anatomical Charts & Posters
The sural region pertains to the posterior leg region. At the distal third of the gastrocnemius, both sural cutaneous branches join to become the sural nerve. It supplies the skin over the posterolateral leg and foot. It is formed by the union of two smaller sensory nerves: Many health conditions can affect your nerve, including.
Sural Nerve Anatomy Anatomical Charts & Posters
It supplies the skin over the posterolateral leg and foot. The medial sural cutaneous nerve (a branch of the tibial nerve ), and lateral sural cutaneous nerve (branch of the common fibular nerve ). At the distal third of the gastrocnemius, both sural cutaneous branches join to become the sural nerve. This union may happen.
suralnervefunction Pivotal Motion Physiotherapy
It is formed by the union of two smaller sensory nerves: The sural nerve is a cutaneous nerve, providing only sensation to the posterolateral aspect of the distal third of the leg and the lateral aspect of the foot, heel, and ankle. Your sural nerve is part of your peripheral nervous system. This union may.
Sural Region Anatomy For more information, please refer to the description of the posterior leg region. The sural region pertains to the posterior leg region. Many health conditions can affect your nerve, including diabetes and sports injuries. Travels posterior to lateral malleolus and deep to fibularis tendon sheath. Your sural nerve is part of your peripheral nervous system.
The Sural Nerve (Sn) Is An Important Pure Sensory Cutaneous Nerve Which Innervates The Lateral Ankle And Foot To The Base Of The Fifth Metatarsal.
It is formed by terminal branches of the tibial and common peroneal nerves that join together in the superficial aspect of the distal third of the leg. Travels posterior to lateral malleolus and deep to fibularis tendon sheath. At the distal third of the gastrocnemius, both sural cutaneous branches join to become the sural nerve. It is formed by the union of two smaller sensory nerves:
Your Sural Nerve’s Length And Ability To Regenerate Make It Ideal For A Sural Nerve Biopsy Or Graft.
The sural nerve is formed by the union of the medial sural cutaneous nerve and the sural communicating branch of the common fibular nerve. Many health conditions can affect your nerve, including diabetes and sports injuries. For more information, please refer to the description of the posterior leg region. The sural region pertains to the posterior leg region.
Descends On The Posterolateral Aspect Of Leg.
Your sural nerve is part of your peripheral nervous system. The sural nerve (sn) is an important pure sensory cutaneous nerve which innervates the lateral ankle and foot to the base of the fifth metatarsal. It supplies the skin over the posterolateral leg and foot. It provides sensation to your lower leg and parts of your foot.
The Sural Nerve Is A Cutaneous Nerve, Providing Only Sensation To The Posterolateral Aspect Of The Distal Third Of The Leg And The Lateral Aspect Of The Foot, Heel, And Ankle.
The sural nerve (s1, s2) is a peripheral nerve that arises in the posterior compartment of the leg (calf or sural region). This union may happen at variable levels in the posterior compartment of the leg. The sural nerve passes through the calf (sural region) superficial to the gastrocnemius muscle and lateral to the calcaneal (achilles) tendon. The sural nerve is a cutaneous nerve of the lower limb, formed by contributions from the tibial and common fibular nerves.